Two-dimensional Analysis
Modelling the Object
Before actually working with the program, a sketch of the object should be prepared in which relevant data is summarised for model input. Such a sketch of the two-dimensional demonstration object would include the information shown below: dimensions, reference coordinates, and material properties.
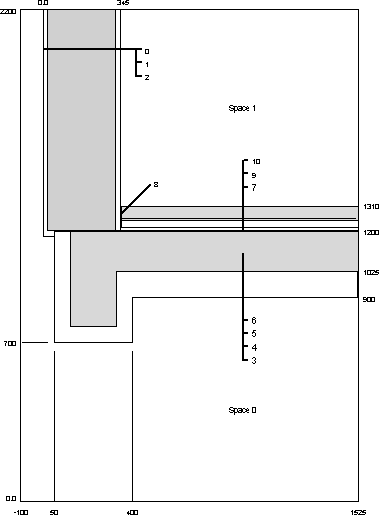
| material | λ [Wm-1K-1] | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | stucco | 0.800 |
| 1 | masonry | 0.164 |
| 2 | interior plaster | 0.700 |
| 3 | exterior plaster | 0.800 |
| 4 | insulation | 0.041 |
| 5 | adhesive mortar | 0.271 |
| 6 | reinf. concrete | 2.200 |
| 7 | sand | 1.000 |
| 8 | expansion strip | 0.150 |
| 9 | isol. underlayment | 0.040 |
| 10 | concrete topping | 1.200 |
| space | α [Wm-2K-1] | |
| 0 | exterior | 25 |
| 1 | interior | 6 |
Since negative coordinate values are allowed, the positioning of the graph origin (x=0, y=0) is generally arbitrary. The reference coordinates shown here, however, are the ones consistent with the geometric input data as related in the next section.
Continue reading with "Generating the Model - Input" ...